Will technology innovation save the planet? As the climate crisis continues and target years loom, scientists and engineers are working together to bring new solutions for energy storage and usage while contributing to a circular economy.
Here are 10 green technology innovations that leverage natural resources in a circular fashion and pull together the research and development to bring actionable solutions to the world.
10. Biomimicry
Mimicking plants and the natural environment is a method of sustainability that is only dreamt of. Scientists are working to capture the regenerative functions of plants and animals, similar to healing a wound or sealing a cut made when pruning a plant. This technology could be used in fibres to enable cuts to patch up minor holes and tears.
9. Molten salt energy storage
Heat is one way in which energy can be stored, meeting a gap in the energy sector that must be filled to reach a renewable energy future. It has been noticed that salt has particularly good characteristics for heat storage, making it a great base for capturing and holding energy.
8. Artificial photosynthesis
Speaking of mimicking plants, scientists and technologists are working together to mimic the effects of photosynthesis through technology. The solutions are expected to amalgamate both sunlight and carbon dioxide to create usable energy—a form of carbon capture that will provide further resources.
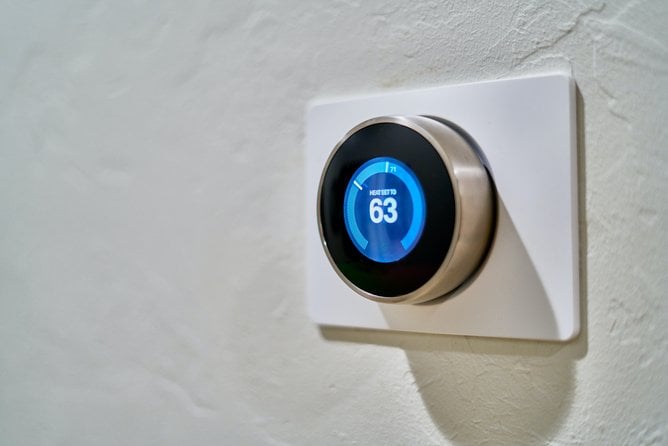

7. Smart meters
While they don’t actively reduce emissions, smart meters installed in homes allowed consumers to reduce their energy consumption, which is an indirect way of reducing overall housing emissions. Individuals are able to save on their household bills while companies have more energy in the pipeline to supply to other buildings.
6. Carbon capture and storage
One of the most innovative solutions for eliminating atmospheric carbon dioxide, carbon sequestration, is going beyond human efforts to plant more trees and reduce carbon output. New technologies will be leveraged in years to come to actively remove carbon emissions from the atmosphere. However, according to the International Energy Agency (IEA), current carbon capture alone will not be enough to deliver the 1.7 billion tonnes of activity required.
5. Electric vehicle propulsion
One of the most visible forms of renewable technology is electric vehicle (EV) propulsion. Range anxiety plays a role in the adoption of EVs as the current charging infrastructure and energy grids are not capable of supporting a fully-electric future, yet.
4. Nuclear energy technology
Although controversial based on its potential to disrupt cities (an example being the Chernobyl nuclear reactor), technology is being developed to make the most of nuclear materials to produce clean energy at scale. Current technicians are only able to utilise uranium supplies to around 1% of their full potential, making nuclear a contender for widespread green energy.
3. Waste-water electricity generator
The circular economy can be applied beyond recycling man-made materials. Oregon State University developed a hybrid electricity generator, which uses microbial fuel cells and reverse electrodialysis. These technologies combined enable the use of waste water to create electricity. Alongside the solutions contribution to mains grid power generation, the technology is also capable of powering the treatment of water as it comes full circle.
2. Recycled plastic road surfacing
In 2021, Coca-Cola announced its road surfacing project in Pakistan as it encourages a circular economy of waste materials. Plastic-based road materials have been adopted as an initiative that not only utilises recycled plastic bottles, but also develops in the community in the surrounding area.
1. Green architecture
Due to the sheer scale of the built environment, difficulties arise around the sustainability of urban living. As buildings are getting taller and cities more compact, innovation is taking place to ensure that new buildings meet climate requirements, but are also capable of generating energy, sequestering carbon, and fitting aesthetically within local landscapes. Initiatives also consist of planted roofs and walls, adding to the carbon reduction footprint.